In the world of nutrition, there’s one unsung hero that doesn’t always get the attention it deserves: fibre. While we often hear about the latest superfoods or trendy diets, fibre quietly plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. So, let’s shine a spotlight on this often-overlooked nutrient and explore why it’s so important to make sure we’re getting enough of it in our diets.
What is Fibre?
Fibre, is a type of carbohydrate found in plant foods that our bodies cannot digest or absorb. Unlike other carbohydrates, fiber passes through our digestive system relatively intact. There are two main types of fiber: soluble and insoluble.
-
Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance. It can help lower blood cholesterol and glucose levels. Sources include oats, barley, nuts, seeds, beans, lentils, and some fruits and vegetables.
-
Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and adds bulk to the stool, helping to prevent constipation and promote regularity. Whole-wheat flour, wheat bran, nuts, beans, and vegetables such as cauliflower, green beans, and potatoes are good sources.
-
The Health Benefits of Fibre
1. Improved Digestive Health
One of the most well-known benefits of fibre is its role in promoting healthy digestion. Insoluble fiber adds bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass through the digestive tract. This can help prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements. On the other hand, soluble fibre feeds the beneficial bacteria in the gut, promoting a healthy gut, which is linked to improved digestion and overall health.
2. Weight Management
Fibre-rich foods tend to be more filling than low-fiber foods, which can help with weight management. When we feel full and satisfied after a meal, we’re less likely to overeat or snack on unhealthy foods.
3. Heart Health
A high-fibre diet has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease. Soluble fibre, in particular, can help lower LDL cholesterol levels by interfering with its absorption in the intestines.
4. Blood Sugar Control
For those with diabetes or at risk of developing it, fibre can be especially beneficial. Soluble fibre slows the absorption of sugar, helping to improve blood sugar levels. This can contribute to better overall glycemic control and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
How to Incorporate More Fibre into Your Diet
Now that we understand the importance of fiber, the next step is to ensure we’re getting enough of it in our daily diet. Here are some simple tips to increase your fibre intake:
-
Eat Whole Grains: Choose whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat, and oats over refined grains.
-
Load Up on Fruits and Vegetables: Aim to fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables at each meal. Be sure to eat the skins when possible, as that’s where much of the fibre is found.
-
Snack on Nuts and Seeds: Keep a stash of nuts and seeds like almonds, chia seeds, or pumpkin seeds for a quick and fibre-rich snack.
-
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of fiber. Add them to soups, salads, or as a main dish.
-
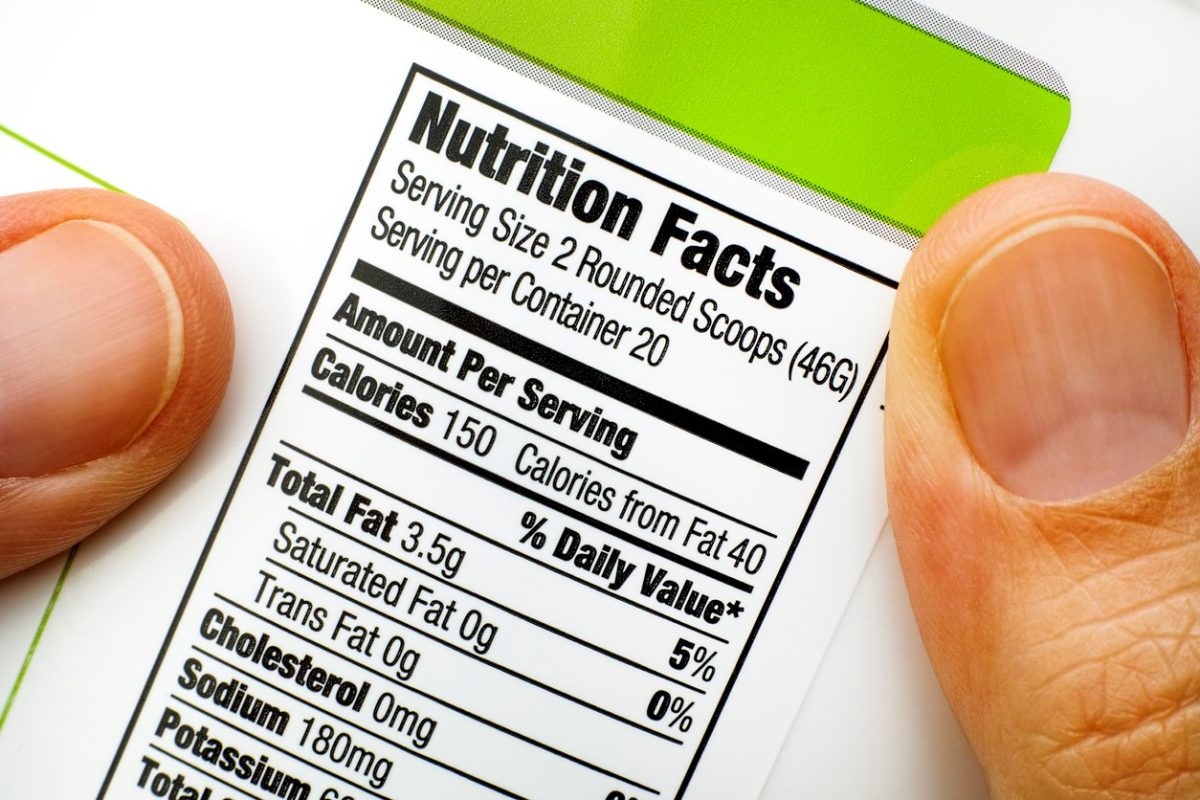
Read Labels: When buying packaged foods, check the nutrition labels for fiber content. Aim for products with at least 3-5 grams of fiber per serving.
In Conclusion
While fibre might not be the most glamorous nutrient, its benefits to our health are undeniable. From promoting healthy digestion to reducing the risk of chronic diseases, fibre plays a crucial role in our overall well-being. By making simple changes to incorporate more fibre-rich foods into our diets, we can reap the rewards of this unsung hero and support our health for years to come. So, let’s give fibre the attention it deserves and make it a priority on our plates
-
Need more support? Email Nicole Byrom here!